CarTrain "First Responder Trainer for Electric Vehicles"
The number of hybrid and electric vehicles on the roads worldwide is steadily increasing. This is not only a new challenge for the workshops, which have to perform the service and also various diagnostic and repair work on the vehicles. In particular, the HV vehicles involved in accidents pose a special challenge and require special qualifications in order to avoid endangering their own lives as well as those of all other parties involved. However, the workshops are only the last link in the chain; the first contact with an HV vehicle involved in an accident is primarily made by the national first responders, such as the police, fire department and recovery services.
These professional groups require equally intensive and target group-oriented training or additional qualification in order to enable proper and safe recovery of the HV vehicles involved in the accident. This is precisely where Lucas-Nuelle's training system comes in, offering the professionals an absolutely safe but at the same time practical training concept consisting of training hardware and a special e-learning course. In this way, they are optimally prepared for the various accident scenarios with HV vehicles and can practice the correct procedure over and over again through the various practical exercises as well as the interactively prepared theory - until this has become second nature. This is essential in order not to make any mistakes and to work in a highly time-efficient manner under time pressure and other disruptive influences.
Competence transfer
Responders will acquire the following competencies:
- Identify hybrid and electric vehicles upon reaching the scene of an accident.
- Identifying HV components in the HV vehicle involved in the accident
- Understanding the real-world hazard potential of HV vehicles (respect, but don't fear!)
- Hazard assessment before beginning recovery
- Procedures for rescuing people from HV vehicles
- Application of personal protective measures against electric body flow
- Securing the vehicle key/shutting off the vehicle electrical system
- Use of rescue cards
- Setting up a rescue card database and preparing it for rapid deployment
- Safe and fast shutdown of the HV system
- Evaluation of the hazard potential of an HV battery (in use)
- Special features of securing the accident site
- First aid measures
- Procedure for damaged HV vehicles
- Hazard assessment before transporting a damaged HV vehicle
- Correct transport of damaged HV vehicles
Scope of delivery
The following components are included in the scope of delivery:
- CarTrain "Accident Assistance and Recovery of HV Vehicles" CO3223-6Z
- E-learning course for Windows systems (PC, laptop, tablet) without license commitment
- Instruction manual
Contents of the E-Learning course
The eLearning course is equipped with numerous videos, animations and images and offers the following thematic contents (overview):
- Types of electric and hybrid vehicles
- Identification of hybrid and electric vehicles
- Identification of HV components in the vehicle
- Main differences between hybrid and electric vehicles
- Hazards associated with HV systems
- Hazards due to damaged HV components
- Hazards associated with damaged HV vehicles
- Safety precautions before starting recovery operations
- Hazards associated with handling HV batteries
- Typical location and arrangement of HV components
- HV disconnect devices
- LV disconnecting devices
- Special NV disconnect devices for rescue workers.
- Identifying the READY state of the vehicle
- Storage of damaged electric and hybrid vehicles
- Safe approach to an electric or hybrid vehicle
- Vulnerable groups in incidents involving electric/hybrid vehicles
- Assessing the extent of HV vehicle damage
- Use of rescue cards
- Access to additional support/information gathering
- First aid in the event of electrocution
- Protection methods for rescuing people and others
- Damaged HV vehicles
- Safe transport and storage of an electric or hybrid vehicle
- Introduction to "Thermal Fuses"
- Smart phone als digital car key
Practical work on the training hardware
The following activities can be performed directly on the hardware:
- Switching on/off the READY mode
- Switching off the HV system via an HV switch-off device
- Switching off the HV system via an NV switch-off device
- Switching off the HV system by means of a special fuse
- Switching off the HV system by means of a cutting solution
- Working/securing a smart key
- Visual inspection of the presence of HV voltages in components of the HV system
- Manufacturer-dependent discharge characteristics of the HV capacitor
- Application of thermal cameras
Practical accident scenarios
The training system offers the possibility to activate various accident scenarios in order to plan and work through the appropriate procedure together:
- Scenario 1: HV system of the vehicle cannot be switched off.
- Scenario 2: Severe damage to the rear (and HV battery).
- Scenario 3: Submerged HV vehicle
- Scenario 4: Burning HV vehicle
- Scenario 5: Trapped driver
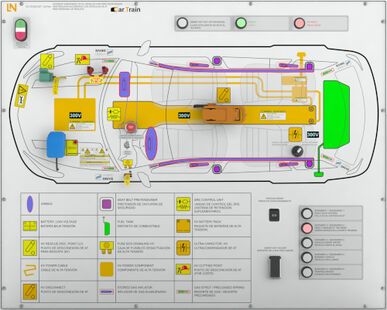
Structure of the training hardware
The training hardware works only with a simulated HV voltage, i.e. the participants have the possibility to learn completely relaxed and concentrated, since even in reality serious mistakes, here no serious consequences bring. The intention of the hardware is to be as practical as possible, which is why the hardware has the following components:
- Representation of the front graphic in the rescue card design
- Use of the symbols according to ISO 17840-1:2015 or the vehicle manufacturer's symbols
- Real HV cut-off device from the vehicle
- Real LV disconnecting device from the vehicle
- Real HV fuse from the vehicle
- Real cutting solution
- Central locking
- Pushbutton for handbrake
- Display of the HV voltages component-related via displays
- Selection of passive or active discharge of the HV condenser
- Safe heating of the HV battery with activated fault scenario
- 12V battery
- Smart Key to activate the vehicle
- Start button and brake button to switch on READY mode
- HV fault indication
- Designations based on ISO 17840-1
Dimensions
- Dimensions: 1000 x 800 x 220mm (WxHxD)
- Weight: approx. 35kg